Top 10 Most Common Problems with International/Navistar MaxxForce Engines (and How to Fix Them)
Aug 30th 2025
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- EGR Cooler Failure
- Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) Problems
- Turbocharger Issues
- Fuel Injector Problems
- EGR Valve Malfunctions
- High-Pressure Oil System Failures
- Cooling System Problems
- Air Intake System Malfunctions
- Electronic Control Module (ECM) Issues
- Exhaust Aftertreatment System Failures
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction
Top 10 Most Common MaxxForce Engine Problems
1. EGR Cooler Failure
- Understanding the EGR System
- Common Symptoms of EGR Cooler Problems
- Root Causes of EGR Cooler Failure
- Repair Solutions and Prevention
2. Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) Problems
- How DPF Systems Work in MaxxForce Engines
- DPF Problem Symptoms
- Causes of DPF Failures
- DPF Repair and Maintenance Solutions
3. Turbocharger Issues
- MaxxForce Turbocharger Design and Function
- Turbocharger Problem Symptoms
- Common Turbocharger Failure Modes
- Turbocharger Repair Solutions
4. Fuel Injector Problems
- MaxxForce Fuel Injection Technology
- Fuel Injector Failure Symptoms
- Causes of Injector Problems
- Injector Repair and Replacement
5. EGR Valve Malfunctions
- EGR Valve Operation in MaxxForce Engines
- EGR Valve Problem Indicators
- EGR Valve Maintenance and Repair
6. High-Pressure Oil System Failures
- MaxxForce High-Pressure Oil System Design
- High-Pressure Oil System Problems
- Common Failure Points
- Repair and Maintenance Solutions
7. Cooling System Problems
- MaxxForce Cooling System Complexity
- Cooling System Problem Symptoms
- Common Cooling System Issues
- Cooling System Maintenance and Repair
8. Air Intake System Malfunctions
- MaxxForce Air Intake Design
- Air Intake Problem Symptoms
- Common Air Intake Issues
- Air Intake System Service
9. Electronic Control Module (ECM) Issues
- MaxxForce Engine Management Systems
- ECM Problem Indicators
- ECM Troubleshooting and Repair
10. Exhaust Aftertreatment System Failures
- MaxxForce Aftertreatment Technology
- Aftertreatment System Problems
- Aftertreatment System Service and Repair
International/Navistar MaxxForce engines have been powering medium and heavy-duty trucks across North America for over a decade. These engines, which include the MaxxForce 5, 7, 9, 10, 11, 13, and 15 models, were designed to meet stringent EPA emissions standards while delivering reliable performance. However, like any complex diesel engine system, MaxxForce engines experience their share of common problems that can leave fleet operators and owner-operators dealing with costly downtime and repairs.
Understanding these common issues and knowing how to address them can save thousands in repair costs and prevent unexpected breakdowns. This comprehensive guide covers the ten most frequent problems plaguing MaxxForce engines, providing detailed explanations of symptoms, causes, and proven solutions. Whether you're a fleet manager, diesel technician, or truck owner, this information will help you maintain your MaxxForce-powered vehicles more effectively.
The MaxxForce engine family was International's answer to increasingly strict emissions regulations. These engines incorporate advanced systems like exhaust gas recirculation (EGR), diesel particulate filters (DPF), and selective catalytic reduction (SCR) technology. While these systems help reduce harmful emissions, they also introduce additional complexity and potential failure points that didn't exist in older, simpler diesel engines.
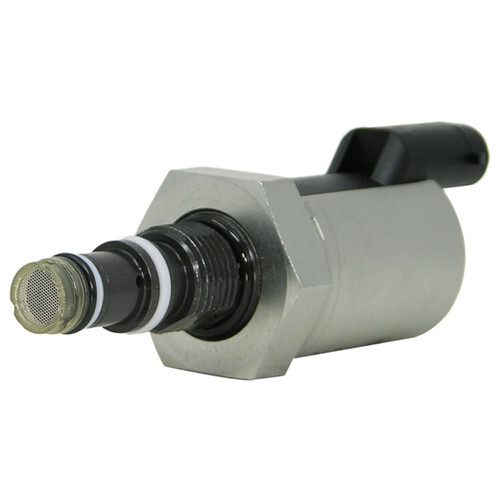

EGR Cooler Failure
Understanding the EGR System
The Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system is one of the most critical components in MaxxForce engines for meeting emissions standards. The EGR cooler functions like a mini radiator, cooling hot exhaust gases before they're recirculated back into the engine's intake system. This process reduces combustion temperatures and helps minimize nitrogen oxide (NOx) formation.
In MaxxForce engines, the EGR cooler experiences extreme temperature fluctuations and corrosive exhaust gases, making it particularly vulnerable to failure. The cooler consists of a series of tubes through which engine coolant flows, surrounded by exhaust gas passages. Over time, these tubes can crack, corrode, or become clogged, leading to various engine problems.
Common Symptoms of EGR Cooler Problems
- White smoke from the exhaust stack, especially during startup
- Coolant loss without visible external leaks
- Overheating issues despite adequate coolant levels
- Reduced engine power and poor fuel economy
- Check engine lights with EGR-related fault codes
- Milky or contaminated engine oil indicating coolant intrusion
- Steam or vapor from the exhaust during operation
Root Causes of EGR Cooler Failure
The primary cause of EGR cooler failure in MaxxForce engines is thermal stress cycling. Each time the engine starts and stops, the cooler experiences rapid temperature changes that cause expansion and contraction. Over time, this cycling creates micro-cracks in the cooler tubes.
Corrosion also plays a significant role, particularly when engines operate on poor-quality diesel fuel or experience infrequent regeneration cycles. Soot buildup in the EGR passages restricts flow and increases temperatures, accelerating cooler degradation. Additionally, using incorrect coolant types or neglecting coolant maintenance can lead to internal corrosion and scale formation.
Repair Solutions and Prevention
Immediate Repair Steps:
- Confirm EGR cooler failure through pressure testing
- Remove the failed cooler and inspect for tube cracks or corrosion
- Replace with a high-quality aftermarket cooler designed for improved durability
- Flush the cooling system completely to remove any contamination
- Replace engine oil and filter if coolant contamination is suspected
- Clear fault codes and perform system tests
Preventive Measures:
- Maintain proper coolant mixture and change intervals
- Use only approved coolant types for MaxxForce engines
- Ensure regular DPF regeneration cycles complete properly
- Address engine overheating issues immediately
- Consider EGR cooler delete options where legally permissible
Pro Tip: When replacing an EGR cooler, always inspect the EGR valve and intake manifold for carbon buildup. Cleaning these components during cooler replacement prevents premature failure of the new part.
Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) Problems
How DPF Systems Work in MaxxForce Engines
The Diesel Particulate Filter is essential for capturing and burning off soot particles from the exhaust stream. MaxxForce engines use an actively regenerated DPF system that periodically heats the filter to extremely high temperatures (around 1,000°F) to burn accumulated soot into ash.
The DPF regeneration process occurs automatically during normal operation, but problems arise when vehicles operate primarily in stop-and-go traffic or short-haul applications that don't allow sufficient time for complete regeneration cycles. This incomplete regeneration leads to soot accumulation and eventual filter plugging.
DPF Problem Symptoms
- Amber or red DPF warning lights on the dashboard
- Reduced engine power and poor acceleration
- Increased fuel consumption during regeneration attempts
- Exhaust system overheating warnings
- Engine derating or limiting maximum RPM
- Black smoke during forced regeneration attempts
- Strong sulfur smell from the exhaust
Causes of DPF Failures
The most common cause of DPF problems in MaxxForce engines is incomplete regeneration cycles. Urban delivery trucks and vehicles used for short trips often don't reach the sustained highway speeds necessary for proper regeneration. This leads to progressive soot loading that eventually overwhelms the filter's capacity.
Fuel quality issues also contribute to DPF problems. Ultra-low sulfur diesel (ULSD) fuel with high aromatic content or biodiesel blends can increase soot production. Additionally, engine problems that cause excessive soot production, such as worn injectors or turbocharger issues, can accelerate DPF loading.
DPF Repair and Maintenance Solutions
Diagnostic Steps:
- Check DPF differential pressure using scan tool
- Review regeneration history and frequency
- Inspect exhaust system for leaks or damage
- Test DPF temperature sensors and pressure sensors
- Evaluate engine operation for excessive soot production
Repair Options:
- Professional DPF cleaning: Remove and clean the filter using specialized equipment
- Filter replacement: Install new DPF when cleaning isn't effective
- Forced regeneration: Use diagnostic software to initiate manual regeneration
- System component replacement: Replace faulty sensors or regeneration components
Preventive Maintenance:
- Ensure vehicles regularly operate at highway speeds for 20-30 minutes
- Use high-quality diesel fuel from reputable suppliers
- Maintain proper engine operation to minimize soot production
- Address engine problems promptly to prevent excessive DPF loading
- Follow manufacturer's regeneration procedures when warning lights appear
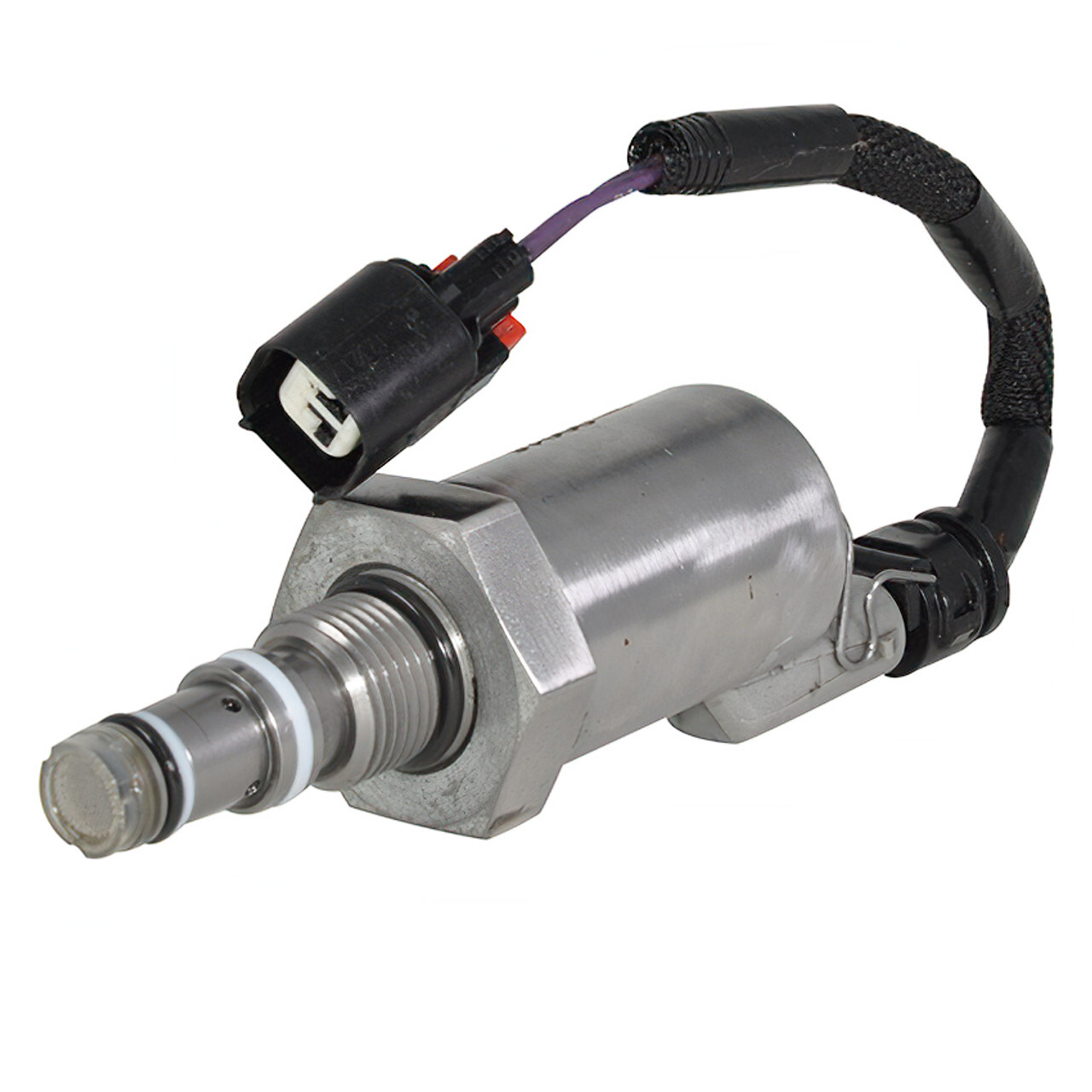

Turbocharger Issues
MaxxForce Turbocharger Design and Function
MaxxForce engines utilize variable geometry turbochargers (VGT) to optimize power delivery across different engine speeds and load conditions. These sophisticated turbochargers use movable vanes to control exhaust gas flow and boost pressure, providing better throttle response and fuel economy compared to fixed-geometry turbos.
The VGT system is controlled electronically and integrates with the engine's overall emissions control strategy. However, this complexity also introduces additional failure modes that don't exist in simpler turbocharger designs. The actuator mechanism, position sensors, and control electronics all represent potential failure points.
Turbocharger Problem Symptoms
- Reduced engine power and sluggish acceleration
- Black or blue smoke from the exhaust
- Unusual whistling or grinding noises from the engine bay
- Oil leakage around turbocharger connections
- Check engine lights with boost pressure codes
- Excessive oil consumption without visible leaks
- Engine rattling at idle or under load
Common Turbocharger Failure Modes
Bearing Failure: The most common turbocharger problem in MaxxForce engines is bearing failure due to oil starvation or contamination. The turbo shaft spins at extremely high speeds (up to 200,000 RPM) and requires clean, pressurized oil for lubrication and cooling.
VGT Actuator Problems: The variable geometry actuator can stick or fail due to carbon buildup or electronic issues. This prevents proper vane positioning and affects boost control.
Compressor Wheel Damage: Foreign object ingestion or bearing failure can damage the compressor wheel, causing vibration and reduced efficiency.
Turbocharger Repair Solutions
Diagnosis Process:
- Check boost pressure using scan tool or pressure gauge
- Inspect air intake system for restrictions or leaks
- Examine turbocharger for oil leaks or damage
- Test VGT actuator operation and position feedback
- Evaluate oil supply and return lines for restrictions
Repair Options:
- Complete turbocharger replacement: Most reliable solution for severely damaged units
- Turbocharger rebuild: Cost-effective for units with bearing or seal problems
- VGT actuator replacement: Addresses variable geometry control issues
- Oil line service: Clean or replace oil supply and drain lines
Prevention Strategies:
- Maintain proper oil change intervals with high-quality diesel engine oil
- Allow proper engine warm-up and cool-down periods
- Address air intake restrictions immediately
- Use quality fuel filters to prevent contamination
- Monitor boost pressure regularly during operation
Pro Tip: Always replace oil and filters when installing a new or rebuilt turbocharger. Contaminated oil is the leading cause of repeat turbocharger failures.
Fuel Injector Problems
MaxxForce Fuel Injection Technology
MaxxForce engines employ high-pressure common rail fuel injection systems that deliver precise fuel metering for optimal performance and emissions control. These systems operate at pressures exceeding 30,000 PSI, requiring extremely tight tolerances and high-quality components.
The fuel injectors in MaxxForce engines are electronically controlled and can fire multiple times per combustion cycle to reduce emissions and noise. This sophisticated operation makes them sensitive to fuel quality issues and contamination that wouldn't affect simpler injection systems.
Fuel Injector Failure Symptoms
- Rough engine idle and misfiring
- Black smoke from the exhaust during acceleration
- Poor fuel economy and reduced power
- Engine knocking or unusual combustion noise
- Difficult starting, especially when cold
- Check engine lights with injector-specific codes
- Excessive white smoke during startup
Causes of Injector Problems
Fuel Contamination: Poor fuel quality is the leading cause of injector problems in MaxxForce engines. Water, dirt, or microbial growth in diesel fuel can damage the precision components within the injectors.
Carbon Buildup: Extended idle periods or low-load operation can cause carbon deposits on injector nozzles, affecting spray patterns and fuel delivery.
Wear and Tear: The extreme pressures and constant operation eventually wear internal injector components, particularly the needle valve and seat.
Injector Repair and Replacement
Diagnostic Procedures:
- Perform cylinder contribution tests to identify weak injectors
- Check fuel pressure and volume delivery
- Inspect fuel quality for contamination or degradation
- Test injector resistance and control signals
- Examine exhaust smoke patterns during operation
Repair Solutions:
- Individual injector replacement: Replace only failed units to reduce costs
- Complete set replacement: Recommended for high-mileage engines
- Professional injector rebuilding: Cost-effective option for repairable units
- Fuel system cleaning: Remove carbon deposits and improve performance
Fuel System Maintenance:
- Use only high-quality diesel fuel from reputable suppliers
- Replace fuel filters at recommended intervals
- Add fuel system cleaner periodically to prevent carbon buildup
- Address fuel contamination immediately
- Consider fuel polishing for stored diesel
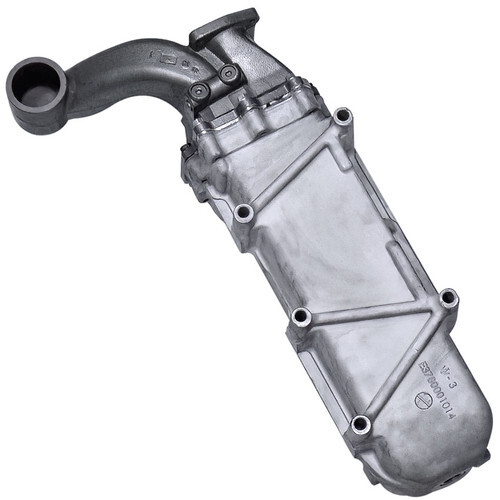

EGR Valve Malfunctions
EGR Valve Operation in MaxxForce Engines
The EGR valve controls the amount of exhaust gas recirculated back into the engine's intake system. In MaxxForce engines, this is typically an electronically controlled valve that modulates flow based on engine operating conditions and emissions requirements.
The EGR valve must operate in an extremely hostile environment, exposed to hot, corrosive exhaust gases while maintaining precise flow control. Carbon buildup from incomplete combustion gradually accumulates on the valve seat and stem, affecting operation and eventually causing failure.
EGR Valve Problem Indicators
- Rough idle and poor engine performance
- Check engine lights with EGR flow codes
- Reduced power and poor throttle response
- Increased emissions and failed inspection tests
- Engine knocking or abnormal combustion noise
- Poor fuel economy and excessive smoke
- Engine stalling or hesitation during acceleration
EGR Valve Maintenance and Repair
Diagnostic Steps:
- Test EGR valve position feedback and control signals
- Check vacuum or electronic actuator operation
- Inspect EGR passages for carbon buildup or restrictions
- Measure EGR flow using scan tool data
- Examine valve seat and stem for wear or damage
Repair Procedures:
- Cleaning: Remove carbon deposits using approved solvents and tools
- Replacement: Install new valve when cleaning isn't effective
- Passage cleaning: Clear all EGR passages and connecting tubes
- System calibration: Perform learn procedures after repairs
- Testing: Verify proper operation across all engine speeds
Preventive Maintenance:
- Regular EGR valve cleaning during major services
- Use quality diesel fuel to minimize carbon formation
- Avoid extended idle periods when possible
- Address engine performance issues promptly
- Consider periodic EGR system cleaning treatments
High-Pressure Oil System Failures
MaxxForce High-Pressure Oil System Design
Some MaxxForce engines, particularly the MaxxForce 7, use high-pressure engine oil to actuate fuel injectors and other systems. This system operates at pressures up to 3,200 PSI and requires special seals, fittings, and components designed for these extreme pressures.
The high-pressure oil pump is typically driven by the engine's camshaft and supplies pressurized oil through a network of internal passages and external lines. Any leak in this system can cause significant performance problems and potential engine damage.
High-Pressure Oil System Problems
- Hard starting or no-start conditions
- Loss of engine power under load
- Rough idle and poor performance
- Oil leaks from high-pressure fittings
- Check engine lights with fuel system codes
- Unusual engine noise during operation
- Oil pressure warning lights or low pressure readings
Common Failure Points
High-Pressure Oil Pump: The pump itself can fail due to wear, contamination, or bearing problems. Internal leakage reduces system pressure and affects injector operation.
O-Rings and Seals: High-pressure seals throughout the system can fail, causing pressure loss and oil leaks. These seals are particularly sensitive to oil quality and temperature.
Injector O-Rings: Each injector has multiple O-rings that seal high-pressure oil passages. These can fail due to age, heat, or oil contamination.
Repair and Maintenance Solutions
Diagnostic Process:
- Test high-pressure oil system pressure using appropriate gauges
- Inspect for external oil leaks at fittings and connections
- Check oil quality for contamination or degradation
- Test individual injector operation and pressure requirements
- Examine high-pressure oil pump operation and output
Repair Procedures:
- Seal replacement: Replace failed O-rings and seals throughout the system
- Pump rebuild or replacement: Address pump failures with quality components
- System flushing: Clean contamination from oil passages and components
- Pressure testing: Verify system integrity after repairs
- Oil and filter service: Always change oil and filters after system repairs
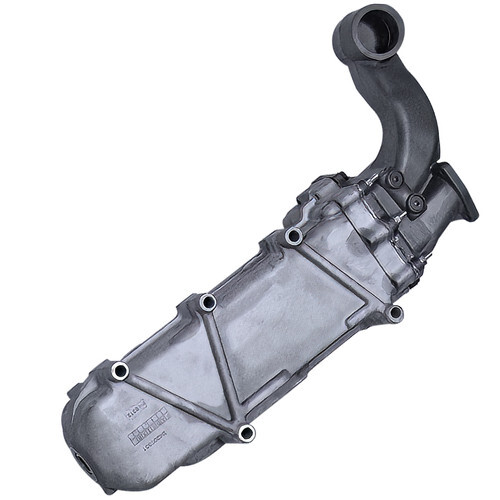

Cooling System Problems
MaxxForce Cooling System Complexity
MaxxForce engines feature complex cooling systems that must manage heat from the engine block, EGR cooler, oil cooler, and aftertreatment components. The cooling system includes multiple thermostats, temperature sensors, and control strategies to optimize performance across different operating conditions.
The integration of emissions control systems places additional demands on the cooling system that didn't exist in older diesel engines. The EGR cooler, in particular, adds significant heat load and introduces potential contamination sources if it fails.
Cooling System Problem Symptoms
- Engine overheating during operation
- Coolant loss without visible external leaks
- Temperature gauge fluctuations or erratic readings
- Reduced heater performance in cold weather
- Steam or vapor from the engine compartment
- Check engine lights with temperature-related codes
- Poor engine performance due to thermal protection
- Coolant contamination or discoloration
Common Cooling System Issues
Thermostat Failures: MaxxForce engines often use multiple thermostats that can fail in open or closed positions, affecting engine temperature control and fuel economy.
Water Pump Problems: High mileage and contaminated coolant can cause water pump bearing or seal failures, leading to coolant leaks and overheating.
Radiator Restrictions: Clogged radiator cores reduce heat transfer capacity, particularly problematic in dusty operating environments.
EGR Cooler Interactions: Failed EGR coolers can contaminate the cooling system with exhaust gases and combustion byproducts.
Cooling System Maintenance and Repair
Diagnostic Approach:
- Test cooling system pressure and capacity
- Check thermostat operation at various temperatures
- Inspect water pump for leaks and proper operation
- Examine radiator and cooling fans for restrictions
- Test temperature sensors and control systems
- Analyze coolant condition and contamination levels
Repair Solutions:
- Component replacement: Replace failed thermostats, water pumps, or radiators
- System flushing: Remove contamination and scale buildup
- Coolant replacement: Use only approved coolant types and mixtures
- Fan and shroud service: Ensure proper airflow through the radiator
- Pressure testing: Verify system integrity and identify leaks
Preventive Maintenance:
- Follow manufacturer's coolant change intervals strictly
- Use only approved coolant types and concentrations
- Inspect cooling system components during regular maintenance
- Address overheating issues immediately
- Keep radiator and cooling fins clean from debris
Air Intake System Malfunctions
MaxxForce Air Intake Design
The air intake system in MaxxForce engines includes turbocharger compressor output, charge air cooling, intake manifold distribution, and various sensors and actuators. This system must deliver clean, properly metered air to each cylinder while accommodating EGR flow and emissions requirements.
Modern MaxxForce engines use sophisticated intake manifold designs with runner tuning and variable geometry features to optimize airflow across different engine speeds. Leaks, restrictions, or sensor failures in this system can significantly affect engine performance and emissions compliance.
Air Intake Problem Symptoms
- Reduced engine power and poor acceleration
- Black smoke from the exhaust during acceleration
- Unusual whistling or hissing sounds from the engine
- Check engine lights with airflow or pressure codes
- Poor fuel economy and increased emissions
- Rough idle or engine hesitation
- Turbocharger overboost or underboost conditions
Common Air Intake Issues
Intake Manifold Leaks: Cracked manifolds or failed gaskets allow unmetered air into the system, affecting fuel mixture and engine performance.
Charge Air Cooler Problems: The intercooler can develop leaks or become restricted, reducing charge density and engine power.
Mass Airflow Sensor Failures: Contaminated or failed sensors provide incorrect airflow data to the engine control module.
Intake Restrictions: Clogged air filters, collapsed intake hoses, or foreign objects can restrict airflow and reduce performance.
Air Intake System Service
Diagnostic Procedures:
- Test intake manifold pressure and vacuum levels
- Inspect all intake connections and hoses for leaks
- Check air filter condition and restriction levels
- Test mass airflow and pressure sensor operation
- Examine charge air cooler for leaks or damage
- Verify turbocharger boost pressure delivery
Repair Solutions:
- Leak repair: Replace gaskets, hoses, or manifold components as needed
- Filter service: Install clean air filters and inspect housing
- Sensor replacement: Replace failed mass airflow or pressure sensors
- Cooler service: Repair or replace charge air coolers
- System cleaning: Remove oil residue and contamination from intake components
Electronic Control Module (ECM) Issues
MaxxForce Engine Management Systems
Modern MaxxForce engines rely heavily on electronic control systems to manage fuel injection, emissions controls, and overall engine operation. The Engine Control Module (ECM) processes inputs from dozens of sensors and controls actuators throughout the engine system.
ECM problems can manifest as various symptoms that may initially appear to be mechanical failures. Software corruption, failed internal components, or communication issues can cause the ECM to operate improperly or fail completely.
ECM Problem Indicators
- Intermittent engine performance issues
- Multiple check engine lights or fault codes
- Engine starting problems or no-start conditions
- Erratic idle or unusual engine behavior
- Communication problems with diagnostic equipment
- Emissions system malfunctions
- Power limitation or engine derating
ECM Troubleshooting and Repair
Diagnostic Steps:
- Verify ECM communication using diagnostic software
- Check power and ground connections to the ECM
- Test CAN bus communication with other modules
- Review fault code history and freeze frame data
- Perform ECM internal tests and calibration checks
- Inspect wiring harnesses for damage or corrosion
Repair Options:
- Software updates: Install latest calibration files and updates
- ECM replacement: Replace failed control modules with programmed units
- Wiring repair: Fix damaged harnesses or connections
- Sensor replacement: Replace failed input sensors affecting ECM operation
- Programming: Perform ECM programming and parameter setup
Exhaust Aftertreatment System Failures
MaxxForce Aftertreatment Technology
MaxxForce engines use comprehensive exhaust aftertreatment systems including diesel oxidation catalysts (DOC), diesel particulate filters (DPF), and selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems. These components work together to reduce harmful emissions but represent complex systems with multiple potential failure modes.
The aftertreatment system requires precise temperature, pressure, and chemical conditions to function properly. Any disruption in these conditions can lead to system failures, reduced performance, and potential engine damage from overheating or chemical contamination.
Aftertreatment System Problems
- Reduced engine power and performance derating
- Exhaust system overheating warnings
- DEF system malfunctions and warning lights
- Regeneration failures or incomplete cycles
- Catalyst efficiency codes and emissions failures
- Exhaust backpressure issues
- Chemical contamination of system components
Aftertreatment System Service and Repair
Maintenance Requirements:
- Regular DEF quality checks and system service
- Periodic exhaust system inspections for damage
- Proper regeneration cycle completion
- Temperature sensor calibration and testing
- Chemical contamination prevention and remediation
Common Repair Procedures:
- Component replacement: Replace failed catalysts, filters, or sensors
- System cleaning: Remove ash and contamination from components
- Software calibration: Update control strategies and parameters
- DEF system service: Clean injectors, replace filters, and test quality
- Regeneration assistance: Perform manual regenerations when required

Frequently Asked Questions
The most costly MaxxForce engine problems typically involve the exhaust aftertreatment system, turbocharger replacement, and high-pressure fuel system failures. Complete aftertreatment system replacement can cost $8,000-$15,000, while turbocharger replacements range from $3,000-$6,000. High-pressure fuel system repairs, particularly when multiple injectors fail simultaneously, can exceed $5,000. EGR cooler failures, while common, are generally less expensive at $1,500-$3,000 for parts and labor.
MaxxForce engines require strict adherence to maintenance schedules due to their complex emissions systems. Oil changes should occur every 15,000-25,000 miles depending on operating conditions, with severe duty applications requiring more frequent service. Fuel filters need replacement every 20,000-30,000 miles, while air filters should be inspected every 15,000 miles and replaced as needed. The DPF system requires regular regeneration cycles, and DEF fluid should be replenished as needed with high-quality product only.
Many MaxxForce engine problems can be significantly reduced through proper maintenance practices. Using high-quality diesel fuel, maintaining clean air and fuel filters, following proper warm-up and cool-down procedures, and addressing warning lights immediately can prevent many common failures. Regular oil analysis can detect problems early, while ensuring complete DPF regeneration cycles prevents expensive aftertreatment system failures. However, some issues like EGR cooler thermal cycling failures are inherent to the design and difficult to prevent entirely.
MaxxForce engines can be reliable in long-haul applications when properly maintained and operated within their design parameters. Highway operation actually benefits these engines by allowing proper DPF regeneration cycles and reducing the thermal stress associated with stop-and-go driving. However, the complex emissions systems require more attention than older, simpler diesel engines. Fleet operators should budget for higher maintenance costs and ensure drivers understand proper operating procedures for emissions systems.
Professional MaxxForce engine diagnosis requires advanced diagnostic equipment capable of communicating with the engine ECM and related control modules. International's ServiceMaxx software provides the most comprehensive diagnostic capabilities, while generic scan tools may offer limited functionality. Essential tools include digital multimeters, pressure gauges for testing various systems, and specialized equipment for DPF pressure testing. Shops servicing these engines should also have access to technical service bulletins and updated calibration files.
Emissions system deletion on MaxxForce engines is illegal for on-road vehicles in the United States and will result in EPA violations and fines. Additionally, deletion typically voids warranties and may cause other engine problems due to changes in operating parameters. Legal compliance aside, modern MaxxForce engines are designed to operate with their emissions systems intact, and removal can actually create more problems than it solves. Focus instead on proper maintenance and addressing root causes of emissions system failures.
Simple maintenance items like oil changes, filter replacements, and basic inspections can typically be performed by knowledgeable owner-operators with proper tools. However, MaxxForce engines require professional service for anything involving the high-pressure fuel system, turbocharger, emissions components, or electronic systems. The complexity of these systems and the potential for expensive damage make professional diagnosis and repair essential. When in doubt, consult with a qualified technician rather than risk costly mistakes.
Properly maintained MaxxForce engines can achieve 400,000-600,000 miles before requiring major overhaul, similar to other modern diesel engines. However, the complex emissions systems may require significant investment in replacement components before reaching traditional rebuild mileage. Many operators find that maintaining the base engine is straightforward, but the aftertreatment systems, turbochargers, and fuel systems require more frequent attention than older diesel designs. Budget for higher per-mile maintenance costs but expect similar overall engine longevity when properly cared for.
