What Is an EGR Cooler? Your Guide to EGR Coolers
Sep 28th 2021

Most modern diesel engines use an exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) emission control system to reduce nitrous oxide (NOx) emissions and improve fuel economy. However, the recirculation process can lead to overheating inside the combustion chamber. That’s why most heavy-duty diesel engines use EGR coolers to reduce the temperature of the exhaust gas before it goes back into the engine, which further decreases cylinder temperatures and NOx emissions.
The EGR system is used throughout the auto industry. It’s used in all types of diesel engines, including light-, medium- and heavy-duty engines as well as low-speed, two-stroke marine engines. Heavy-duty diesel engines have been using this technology since the 1970s, but cooled EGR didn’t go mainstream until the early 2000s.
For commercial heavy-duty diesel engines, EGR is mostly used to reduce NOx emissions, but it has other benefits as well, such as improving engine performance and reducing wear and tear.
If you’re new to this technology, learn more about EGR coolers, how they work, what causes them to fail and what to do if you need a replacement.
What Is an EGR Cooler?
Nitrous oxide forms when extreme heat combines nitrogen and oxygen. If the combustion chamber gets too hot, the heat will break down the chemical bond, which forms new molecules and releases NOx into the air. This is one of the most dangerous pollutants in the world, which is why automakers have gone to great lengths to prevent it. Nitrous oxide can lead to smog, which reduces air quality and can harm those with respiratory conditions. It can also turn into acid rain when mixed with water and air, which isn’t good for anybody.
So, how do diesel engines prevent the spread of NOx?
The EGR system lowers the temperature of the combustion chamber by diluting the air/gas mixture with inert exhaust gas, which reduces the chances of pollution. But this may not be enough to prevent extreme heat.
The EGR cooler injects a coolant to lower the temperature of the exhaust gas before it gets recirculated into the engine intake valve, so the EGR system doesn’t have to work as hard to prevent NOx.
The cooler is located in between the turbo and EGR valve, which connects the engine’s intake valve to the exhaust valve. The EGR system uses a hollow tube, or series of tubes, to recirculate the gas back into the engine. The cooler passes through a series of tubes next to the EGR valve. Heat passes through a wall separating the coolant from the exhaust. This creates an inert, cool exhaust gas, which will lower the temperature of the combustion chamber.
The EGR cooler is controlled by the vehicle’s built-in computer via the EGR valve. The system automatically dispenses coolant based on the temperature of the combustion chamber. The heat is then transferred to the vehicle’s cooling system, which dilutes the excess heat using the radiator.
Shop for Quality Replacement EGR Coolers
What Causes EGR Failure?
As you can see, the EGR cooler is a key part of your engine emissions control system. If your cooler fails, the system won’t be able to control the flow of coolant as the exhaust passes through the EGR valve. This could lead to overheating, the spread of pollution, coolant leaks and excess wear and tear.

EGR coolers fail when the engine puts too much stress on the EGR valve. The exhaust gas can wear down the walls of the coolant valve if it gets too hot, which is usually a symptom of overuse. This breaks down the connection between the exhaust and coolant, so the gas passes back into the engine at a higher temperature than normal.
The coolant can also fail if the EGR valve puts too much pressure on the coolant valve. The cooler cools down the exhaust gas when the EGR valve is closed. The gas reheats when the valve is open. This happens over and over again during a normal drive cycle. Every time the valve heats up, the metal inside the cooler grows and strains against the metal shell. This puts pressure on the entire system.
The turbo may also be a part of the problem. The vehicle’s computer regulates how much boost the engine needs. Lowering the boost reduces the flow of the EGR valve, which puts less stress on the cooler. Increasing the boost increases the flow of the EGR valve, which puts added stress on the cooler.
Your vehicle’s water pump also plays a crucial role by sending water to the EGR cooler. If there’s a problem with the pump, it won’t be able to send water to the cooler, which can lead to overheating. Some engines, such as the Powerstroke 6.0L, use an oil-based coolant, which can lead to clogging in the pump or cooler.
The cooler will also fail if the engine produces high levels of soot, which will then clog and plug your EGR cooler. This is often caused by long idling times and the use of low-sulfur diesel fuel.
Some EGR coolers just aren’t built to last. Many factory diesel engines come with thin, oval shaped EGR coolant valves. This increases the chances of failure as excess heat and pressure disintegrate the walls of the valve.
Poorly designed coolers may not transfer heat correctly or efficiently. Many manufacturers will test their parts in the lab without knowing how they will perform on the road, especially after heavy towing or long trips. Many coolers are placed high on the exhaust valve, which makes them more susceptible to rising temperatures and hotspots.
There could also be an issue with the radiator. If the vehicle can’t get rid of excess heat, the EGR valve will start to overheat. This is often caused by poor airflow. There could be a bag or piece of clothing blocking the radiator.
The EGR cooler can also run out of coolant, which essentially renders it useless.
Any one or combination of these events will put added heat and pressure on the EGR cooler, increasing the chances of failure.

Signs That Your EGR Cooler Needs Replacement
If the EGR valve isn’t working properly, it could lead to expensive repairs or total engine failure. Replacing this small part is often the easiest way to keep your engine running as smoothly as possible.
That’s why it’s important to watch out for warning signs that your EGR cooler is failing.
Watch out for white exhaust steam or smoke coming out of the tailpipe. This usually means the cooler is either cracked or leaking due to gasket failure. If the coolant seeps out of the valve, it will mix with the exhaust and start to boil as it moves through the engine, which causes the gas. It could also mean there’s condensation on the cooler, which can lead to steam.
A leak is a leak. If your EGR cooler is cracked or leaking, you’ll have to replace your coolant more often than you would normally, due to all the waste. If you notice your engine is gobbling up more coolant than normal, the cooler may be broken.
The EGR valve will turn black over time as carbon builds up in the tube. If the cooler fails, coolant will start to mix with the carbon, which creates a sticky, tar-like substance. Watch out for dirty or sticky surfaces when examining your engine. If you have a serious leak, the coolant may wash away the carbon entirely, leaving you with a clean EGR valve. If the valve looks wet or moist, you probably have a leaky cooler.
If the cooler is cracked or leaking, there’s also a chance the exhaust gas will leak into the EGR cooler. This can push coolant out of the overflow bottle, which leads to overheating.
If you have a leak and too much coolant enters the engine intake valve, it could lead to what’s known as hydro-locking, which damages the internal components of your engine. Coolant doesn’t compress like air and fuel, which puts added pressure on the combustion chamber, including gaskets, rods and bolts.
EGR valve and cooler leaks often activate the “Check Engine” light. Check the EGR system when inspecting your engine.
Shop for Diesel Parts by Vehicle Make and Model
How to Prevent EGR Cooler Failure
The best way to prevent EGR cooler failure is to regularly clean and maintain your EGR cooler and engine.
Get rid of soot and other debris that can decrease airflow or clog the cooler.

The inside of the cooler may be dirty as well, especially if your vehicle uses an oil-based cooling system. To remove and clean the filter, you’ll need to soak the part in some detergent until the debris dissolves. Once the part is clean, let it dry before reinstalling.
It’s best to use a special EGR cooler cleaner to get rid of debris, but some experts use all-purpose cleaners or whatever they can get their hands on. EGR cooler detergents tend to be the best when it comes to removing carbon build-up, but some of these products may be slow acting. You should never use flammable cleaning materials, as they may ignite inside the engine.
Make sure all debris and detergent has been removed before reinstalling the part.
If you need help cleaning the cooler, visit your local mechanic for assistance. Some auto shops use ultrasonic technology to send vibrations through the cooler, which usually cleans in just a few minutes.
Use your judgment when setting a cleaning schedule. It all depends on how much you tow and how much stress you’re putting on the engine. Some drivers may need to flush out the EGR cooler every 10,000 miles.
Replacing Your EGR Cooler
If your factory EGR cooler fails, you’re not alone. Many diesel engine owners find themselves having to replace their EGR valve after heavy usage or engine problems.
Experts say most EGR coolers last up to 80,000 miles, but that varies greatly based on the part manufacturer and your driving habits.
When it’s time to replace your EGR cooler, start by finding a diesel parts retailer near you or online. Most vendors let you search by make and model, so you can easily find a replacement EGR cooler that works with your vehicle. It’s best to shop by manufacturer so you don’t have to worry about the part not working with your vehicle. For example, shop for Cummins EGR coolers if you own a Cummins diesel engine.
You’ll also need to choose the right part based on the size of your engine.
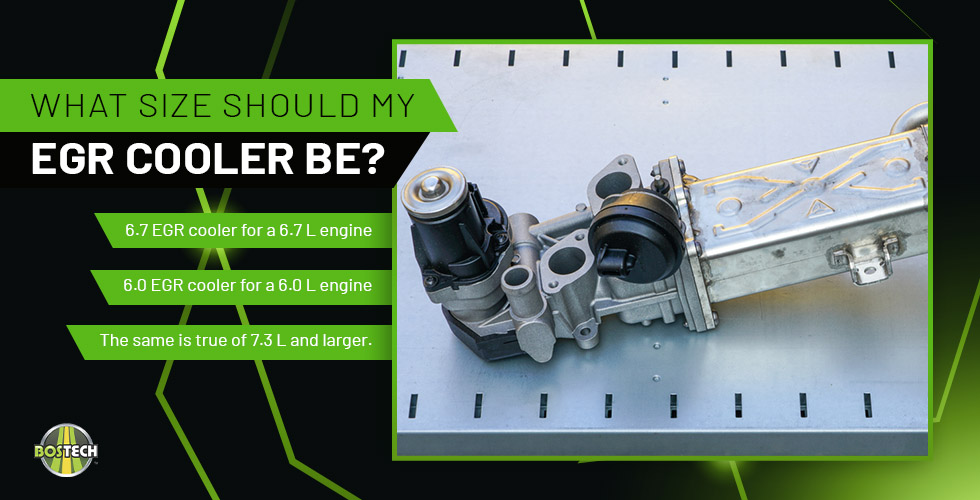
Use a 6.7 EGR cooler if you have a 6.7 L engine. Use a 6.0 EGR cooler if you have a 6.0 L engine. The same is true of 7.3 L engines and larger.
You should only buy replacement parts from reputable retailers with a long history of helping their customers find what they’re looking for. Watch out for counterfeit parts and imitations that may damage your vehicle.
Installing the replacement part can be time-consuming and complicated, depending on the make and model. If you don’t have experience installing the part, it’s best to visit your local mechanic before moving things around under the hood.
Shop Diesel Exhaust System Components
The EGR cooler is an important part of any diesel engine system. It’s here to make your vehicle run as efficiently as possible, while keeping toxic gases out of the air.
Driving without an EGR cooler could lead to serious engine damage as the exhaust overheats. Be sure to maintain this part over time as you continue putting pressure on your engine.
Don’t wait until your current EGR cooler fails to find a replacement. Start looking for quality diesel parts that will last the test of time.
Image Sources
Majrandy/Shutterstock.com
Zigmunds Dizgalvis/Shutterstock.com
Evgenii Panov/Shutterstock.com
OlegRi/Shutterstock.com
gunsan gimbanjang/Shutterstock.com
Minerva Studio/Shutterstock.com
