How Does a Turbocharger Work?
Sep 18th 2023

Shutterstock.com / Sanit Fuangnakhon
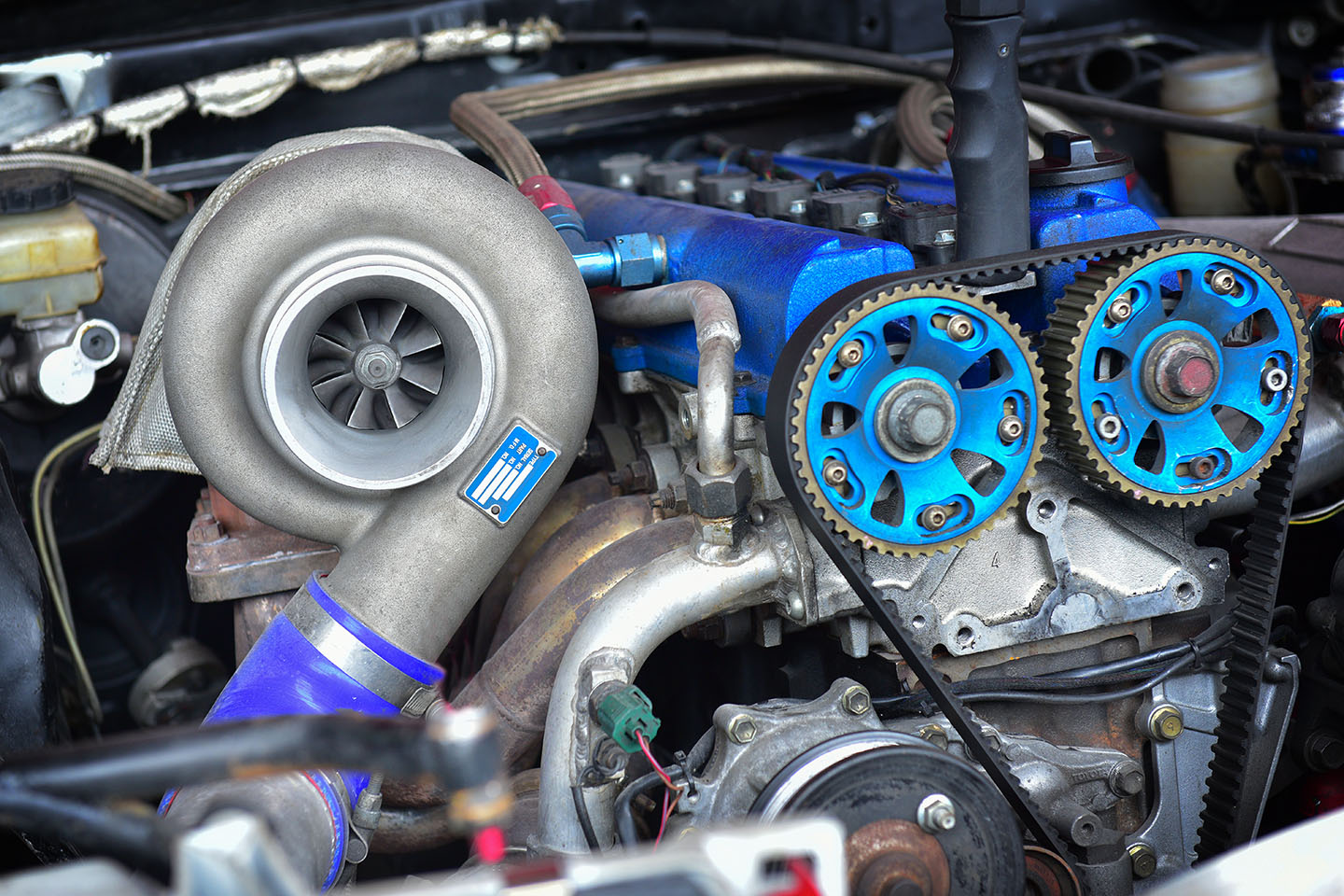
Most modern diesel engines come with a surprisingly useful tool that gives you a much-needed boost behind the wheel. It’s called the turbocharger, which plays a vital role in powering the engine. But this part is more complicated than it seems. It requires regular care and attention, or it could end up doing more harm to your vehicle than good. But how does a turbocharger work and how does it affect your engine?
What Is a Turbocharger?
The turbocharger is designed to increase efficiency and power by delivering more compressed air to the engine, which allows it to burn more fuel, thus generating more energy. Automakers use the turbocharger to increase the output without increasing the size of the engine. This keeps the system compact, which reduces the overall weight of the vehicle. Reducing the size of the engine will help you save on gas. Turbocharged engines tend to produce just as much power as naturally aspirated engines while using less fuel. The turbo will also come in handy when you’re towing heavy loads from rest or uphill.
Shutterstock.com / Scharfsinn
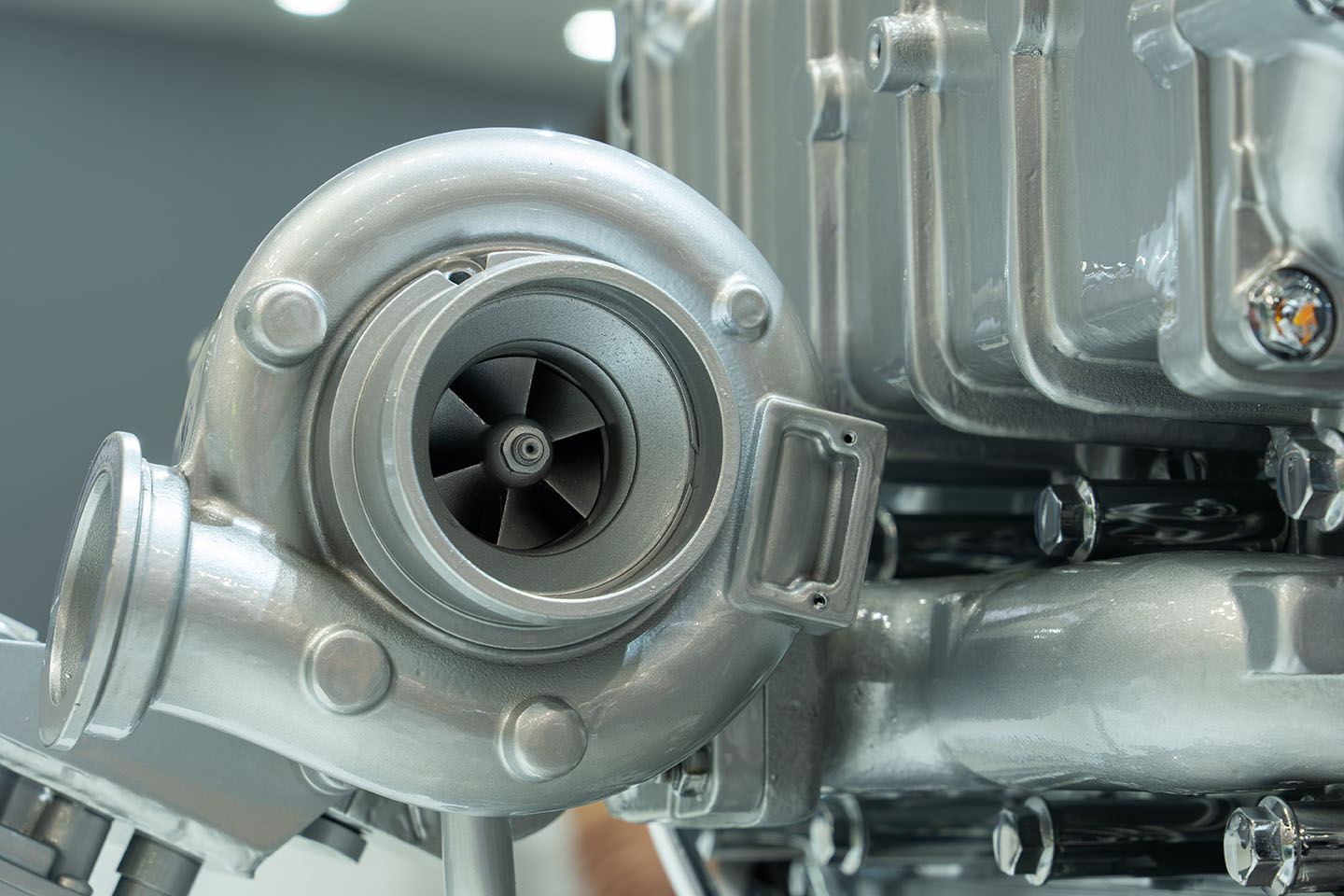
How Does It Work?
The turbocharger brings in exhaust gas via the turbine housing. The gas then turns the turbine wheel, which powers the compressor. The compressor works opposite the turbine housing. The two are linked by a forged steel shaft. The compressor wheel draws in the air to create pressure before sending it into the combustion chamber where it mixes with the pressurized fuel. The glow plugs heat the air and fuel, turning it into mechanical power.
Further Information:Do diesel engines have spark plugs?
As more air enters the turbine, the more it gets compressed. Once the fuel-air mixture burns, a portion of the exhaust gas gets recycled through the engine. The heat from the exhaust gas powers the turbocharger naturally without drawing energy away from the engine. It’s like getting free power from the heat the engine already created. The turbocharger actuator controls the amount of air going through the turbine to make sure the engine gets the right amount of air. It diverts excess exhaust away from the turbine to prevent the engine from burning more fuel than necessary.

Shutterstock.com / Comedstock
If the turbocharger actuator gets clogged, it can damage the engine by overloading it with too much-compressed air. It comes with a spring that holds the wastegate shut until the air reaches the right pressure. Foreign objects can block the pressure release valve, which can cause the entire turbo to break down. Replace the turbocharger actuator if you’re burning through more fuel than usual or suddenly lose power when boosting.
Shop All of Our Oil System Products
Your turbocharger also needs a steady supply of high-quality oil to do its job. It keeps the turbine and compressor lubricated, so they don’t rust over time. Expect to go through more oil than normal if you regularly use the boost feature. Change your oil at or before the recommended interval to avoid damaging these parts.
Even with the best maintenance, a turbo isn’t meant to last forever. It will likely give out before your truck is ready to retire. Most turbos last anywhere from 150,000 to 200,000 miles depending on wear and tear. Riding without a working turbo is a recipe for disaster. You risk damaging your engine by forcing too much-compressed air into the combustion chamber. This will reduce fuel efficiency and power, slowly reducing the output of your engine.
Replace your diesel turbocharger as these warning signs appear to prevent completely ruining the vehicle. Don’t forget to change your exhaust and air filters as needed to stop debris from going through the turbo. Keep the area clean to deliver a steady boost to the engine when you need to accelerate.
